Since February 2022, a malicious campaign has targeted Android users by deploying apps designed to steal SMS messages and intercept one-time passwords (OTPs) for online account verification. This large-scale attack has deployed over 107,000 unique malware samples, wreaking havoc worldwide.
How the Malware Works
These malicious apps are not your typical Play Store downloads. Instead, they appear through deceptive ads mimicking legitimate app listings or via Telegram bots posing as trusted services like Microsoft Word. Once a user is tricked into installing one of these apps, it requests access to incoming SMS messages. Upon gaining this access, it contacts one of 13 command-and-control (C2) servers to transmit the stolen messages.
A Global Threat
The scale of this attack is enormous, with victims detected in 113 countries. India and Russia top the list, followed closely by Brazil, Mexico, the U.S., Ukraine, Spain, and Turkey. This widespread campaign shows how cybercriminals can reach users across the globe, using sophisticated methods to distribute their malware.
The Mechanics Behind the Malware Attack
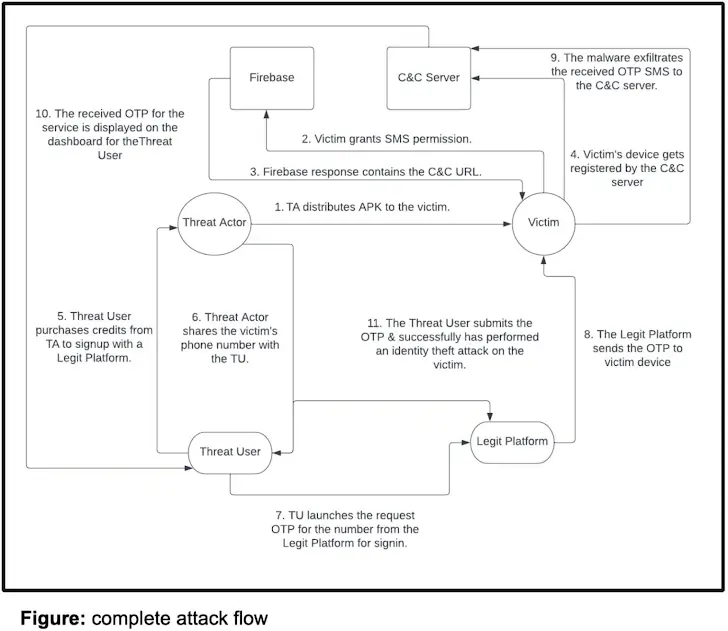
Once installed, the malware hides itself and constantly monitors new incoming SMS messages. Its primary goal is to intercept OTPs used for two-factor authentication (2FA) on various online accounts. This allows the attackers to commit identity fraud by using the OTPs to register for online services without the owner’s knowledge.
Also read | How Cybercriminals Are Using Free IT Tools and YouTube Videos to Spread Malware
Who’s Behind the Attack?
Although it’s unclear who exactly is behind this operation, researchers have observed that the threat actors accept various payment methods, including cryptocurrency. They use these payments to fuel a service called Fast SMS (fastsms[.]su), which sells access to virtual phone numbers.
The Broader Implications
The stolen credentials serve as a springboard for further fraudulent activities, such as creating fake accounts on popular services. This, in turn, can lead to phishing campaigns or social engineering attacks. The findings highlight the continued abuse of Telegram, a popular instant messaging app with over 950 million monthly active users, by malicious actors for different purposes, ranging from malware propagation to C2.
Other Notable Malware Attacks
In early 2022, Trend Micro highlighted a similar financially-motivated service that corralled Android devices into a botnet. This botnet was used to register disposable accounts in bulk or create phone-verified accounts for conducting fraud and other criminal activities. Additionally, Positive Technologies recently disclosed two SMS stealer families, SMS Webpro and NotifySmsStealer, targeting Android users in Bangladesh, India, and Indonesia to siphon messages to a Telegram bot.
Protecting Yourself
Google has stated that Android users are automatically protected against known versions of this malware via Google Play Protect, which is enabled by default on devices with Google Play Services. However, staying vigilant and avoiding installing apps from unknown sources is crucial to safeguarding your personal information.
The Ongoing Battle
The popularity of Telegram and its use as a corporate messenger make it an attractive target for cybercriminals. As a result, threat actors can use it to deliver malware and steal confidential information. Security researchers continually work to uncover these threats and protect users from falling victim to such attacks.
Stay safe, stay informed, and always be cautious of the apps you install on your devices. The fight against cybercriminals is ongoing, but with awareness and vigilance, we can all play a part in securing our digital lives.
Also read | Hackers Use New QR Code Phishing Tactics to Target Organizations