New research reveals a major Google OAuth Vulnerability issue in Google’s “Sign in with Google” feature. This flaw allows attackers to misuse domain ownership changes and access sensitive user data. Truffle Security, a cybersecurity company, highlighted this in a detailed report.
What Is Google OAuth Vulnerability?
Google’s OAuth system lets users log in to apps using their Google accounts. This process involves sharing basic details like email addresses and domain information. The problem arises when someone buys a defunct startup’s domain. This allows attackers to recreate old employee accounts. These recreated accounts can then log in to apps like ChatGPT, Slack, Notion, Zoom, and HR systems.
Attackers cannot access old emails. However, they can misuse the recreated accounts to retrieve sensitive data stored in these apps. HR systems hold critical details like tax documents, social security numbers, and salary information. Interview platforms might store private details about candidates, including feedback and offer letters.
How Does OAuth Work?
OAuth stands for Open Authorization. It is a method that allows apps to access user data from other platforms securely. It uses access tokens instead of passwords to grant access.
When users select “Sign in with Google,” their email and domain are shared with the app. If the app relies only on these details, attackers can exploit domain changes to gain access.
Why Is OAuth Vulnerability a Big Deal?
When startups fail, their domains often go up for sale. If attackers buy these domains, they can recreate employee accounts. This makes them appear legitimate to various apps and services.
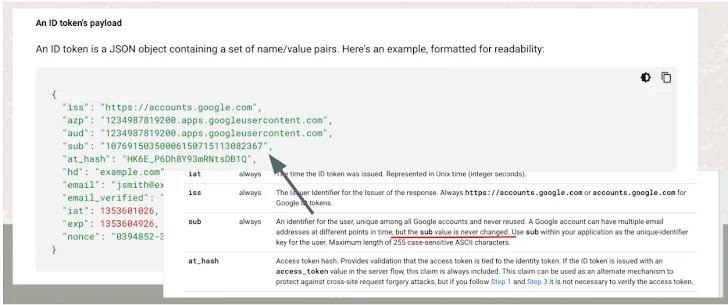
Truffle Security also discovered that Google’s ID tokens include a unique identifier called the “sub claim.” This feature could prevent such attacks. However, it is not always reliable.
Unlike Google, Microsoft’s Entra ID tokens store immutable user values. This makes Microsoft’s system more secure against such threats.
Also read | AI-Powered Ransomware FunkSec Hits 85 Victims Globally
Google’s Response
Initially, Google claimed that this issue was part of the system’s intended design. However, after further review, Google reopened the case in December 2024. The company awarded a bounty of $1,337 to Dylan Ayrey, the researcher who disclosed the flaw.
Google called the issue a “high-impact abuse-related methodology.” The company emphasized best practices to mitigate risks. Users should delete data from third-party apps when closing accounts. Software providers should use unique identifiers like the “sub claim” for user authentication.
A Google spokesperson thanked Ayrey for identifying this risk. They urged businesses to follow best practices when shutting down domains. Deleting SaaS services linked to old domains can prevent unauthorized access.
What Should Businesses Do?
Startups should properly close their domains when shutting down. This prevents attackers from misusing them. SaaS providers must implement better security practices. Using unique identifiers can prevent unauthorized access by users.
Also read | Double Clickjacking: New “Double-Click” Attack to Hack Websites
What Can Individuals Do?
Individuals should ensure their accounts are secure when leaving a startup. After off-boarding, data protection is no longer in their control. The fate of their data depends on the company’s practices and domain security.
Conclusion
The Google OAuth vulnerability is a wake-up call for better security practices. Startups, software providers, and individuals must act to protect sensitive data. Misusing failed domains poses a serious risk to millions of users.
Organizations should adopt security measures like immutable user identifiers. Users must ensure their data is safe when leaving any workplace. Together, these efforts can reduce risks and protect valuable information.

